Maxillofacial surgery
Treatment of neoplasms of the parotid salivary glands
The main thing to know about neoplasms in the parotid region is that they will not go away by themselves. If a suspicious lump appears near the ear or on the lower jaw, you should make an appointment with a maxillofacial surgeon as soon as possible, even if there is no pain or inflammation. We at the Sirius Dent Medical Center have considerable experience in diagnosing and removing tumor-like formations of the head and neck with a minimal risk of recurrence, and if necessary, we refer to an oncologist.

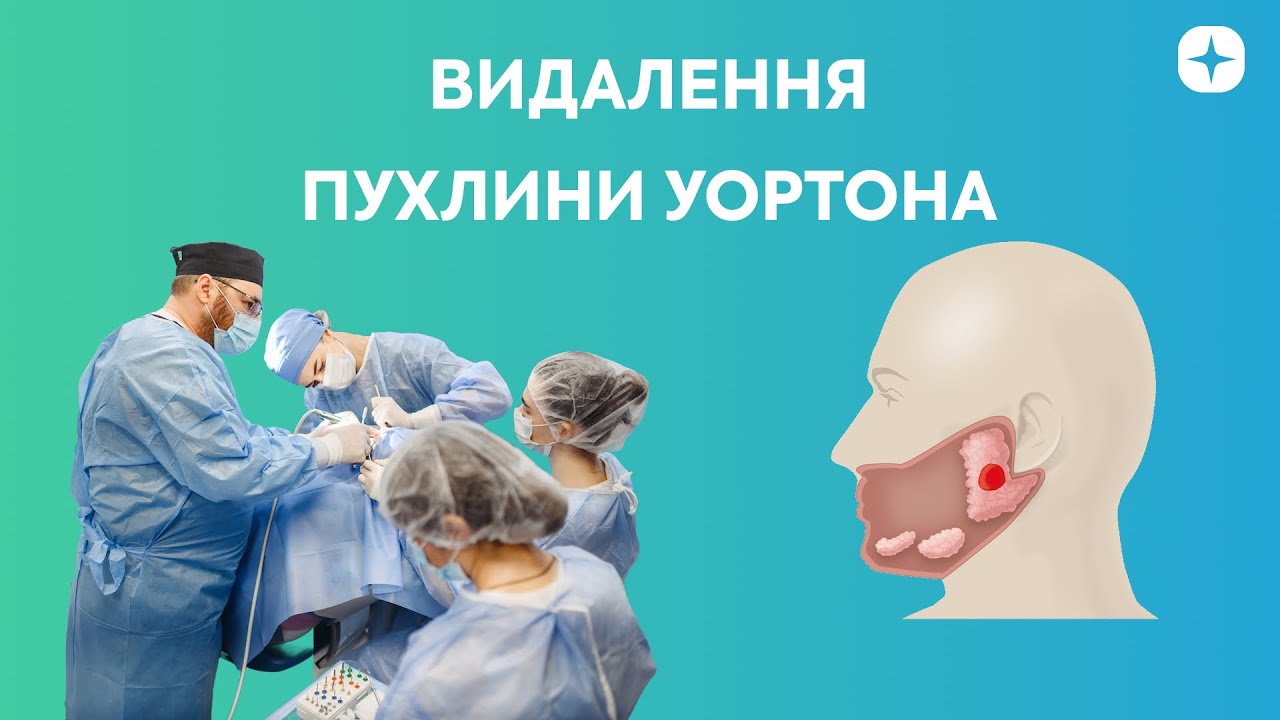
A difficult case. Removal of Wharton's tumor
The difficulty of surgical treatment of Wharton’s tumor lies primarily in its location. It has a very complex anatomical localization: it is surrounded by an ascending branch from the subclavian vein.
The goal for the Sirius Dent Medical Center surgical team under the leadership of the dent medical center’s chief physician, maxillofacial surgeon with more than 20 years of experience in operations, Denys Vyacheslavovich Valkevich, was to preserve the parotid salivary gland itself and to remove only the tumor in isolation.
Patient stories
Many years of experience in the treatment of neoplasms
Call our administrator and make an appointment for a consultation by phone +38 (066) 125 86 31 or fill out the form on the website.

what is worth knowing
What is a neoplasm of the parotid area
In the parotid region (under the ear in the direction of the cheekbone, under the earlobe, at the corner of the lower jaw under the ear or actually under the lower jaw), various, mostly benign, neoplasms appear quite often, which look like lumps and usually do not cause discomfort, except for aesthetic ones. It can be one of the following types of benign neoplasms:
- salivary gland cyst — a tumor-like formation with liquid content;
- Wharton’s tumor (adenolymphoma) — a formation with a complex anatomical location with altered fatty tissue inside;
- pleomorphic adenoma is the most common benign neoplasm around the salivary gland in adults, which has a tendency to transform into a malignant carcinoma.
If the bump under the ear does not bother you, many people walk around with it for years. When it comes to a cyst that is not prone to transformation, delaying visits to the maxillofacial surgeon may not be a big problem, but if it is a neoplasm with a tendency to malign, the passage of time increases the chances of developing cancer. However, only a doctor can determine what kind of neoplasm it is and whether it is an oncopathology.
Given that the number of malignant tumors has been increasing dramatically in recent years, a lump near the ear or under the jaw should not be ignored in any case. If something similar appears, you should contact specialized specialists.
Reasons for the appearance of neoplasms of the parotid area
Currently, it is not known why neoplasms of the salivary glands appear, but we can say for sure that it is impossible to reduce the polyetiological process to one root cause. However, such factors as deterioration of the environment, a decrease in the quality of nutrition, an increase in the level of stress, disruptions in the endocrine system, and heredity play a role in the increase in the number of tumor-like formations, including malignant ones.
What will happen if the neoplasm of the parotid area is not treated
In the case of neoplasms of the parotid salivary glands, time is of the essence: the earlier you come to the doctor, the easier the treatment will be and the lower the risk of missing the cancer. The consequences of untimely referral to a maxillofacial surgeon may vary depending on the diagnosis:
- a benign tumor of the salivary gland will grow in volume, so it will be more difficult to remove it over time;
- the cyst will also grow, but it is also prone to suppuration, so inflammation of the salivary gland will periodically occur;
- pleomorphic adenoma can turn into a malignant tumor.
If the neoplasm is located under the ear in the projection of the parotid salivary gland, then this is also the exit point of the facial nerve, so the task of the surgeon is to remove the tumor so as not to touch the nerve and not harm the patient. Accordingly, the smaller the size of the tumor, the easier it is to operate and the lower the risk for the patient.
Early diagnosis of carcinoma is extremely important: early detection of cancer gives a higher probability of overcoming the disease.
Diagnosis of neoplasms of the parotid area
First of all, it is necessary to establish exactly what neoplasm we are dealing with. Therefore, we usually start with computer tomography, which helps to determine the scope of the future operation and optimal access. Ultrasound examination in this case is not informative, because it gives information only about the size and presence of a neoplasm, which can also be determined visually and by palpation. If there is a suspicion of a malignant tumor, additional studies are prescribed: a puncture from the neoplasm under ultrasound control (cytological diagnosis of salivary gland tumors), which is performed by an oncologist, CT with contrast and CT of the lungs, because these tumors quickly metastasize to the neck lymph nodes and lungs.
When we have made sure that it is really cancer, the patient with the entire package of documents and the surgeon’s note is sent to the Feofania medical centeral hospital, where a council of leading specialists determines the optimal tactics of complex treatment (combined surgery and chemotherapy).
We remove benign neoplasms (cyst, Wharton’s tumor, adenoma) directly in our dent medical center.

Treatment of neoplasms of the parotid area
All neoplasms of the parotid and submandibular region are treated surgically. It is important to use the correct technique and tactics for complete removal of the neoplasm. Thus, if the cyst is simply opened and the fluid that has accumulated inside is removed, this will lead to its re-filling. Therefore, it should be removed completely, including the shell, to get the desired result. Similarly, other benign tumors should be operated on.
Rehabilitation after the removal of a salivary gland tumor usually goes smoothly, often the patient does not even need to be hospitalized and can go home in the near future.
If cancer is diagnosed, it is necessary to radically remove the tumor along with healthy tissues, retreating to a certain distance to avoid recurrence. Often, the entire gland is removed, because a malignant tumor does not have clear borders, and its protrusions enter the adjacent tissues. After surgery, the tumor is sent for histology, based on the results of which an immunohistochemical study is performed. It helps to choose the right chemical drugs for further therapy. Next, a council of doctors decides what the next steps will be, depending on the type of tumor, the age of the patient and the state of his body.
Prevention of neoplasms of the parotid area
Since the exact risk factors for the development of salivary gland tumors are currently unknown to science, there are no ways to prevent this. In any case, it is important to immediately consult a maxillofacial surgeon if you notice a lump in the parotid or submandibular region.
When it is necessary to consult a doctor for the treatment of neoplasms of the parotid salivary glands
The sooner you see a doctor about a neoplasm of the parotid salivary gland, the easier it will be to remove it. This does not mean that you have to urgently consult a surgeon on the same day – if you wait a week, most likely, trouble will not happen. But it’s definitely not worth walking around with a bump near your ear for years. The main thing is that you should not even try to use traditional medicine against the lump or to clean the gland at home, it will at least not work, and at the most it will harm.
- What is a neoplasm of the parotid area
- Reasons for the appearance of neoplasms of the parotid area
- What will happen if the neoplasm of the parotid area is not treated
- Diagnosis of neoplasms of the parotid area
- Treatment of neoplasms of the parotid area
- Prevention of neoplasms of the parotid area
- When it is necessary to consult a doctor for the treatment of neoplasms of the parotid salivary glands
- Who provides this service
who provides this service
Patient reviews
Popular questions
Who treats a salivary gland tumor?
A maxillofacial surgeon treats various neoplasms and inflammation of the salivary gland (sialoadenitis) and other soft tissues of the face.
What causes a tumor of the salivary gland?
A salivary gland tumor is not only a cosmetic defect: it continues to grow slowly, sometimes becomes inflamed and, in the worst case, can turn into cancer. All this can be avoided if you contact a maxillofacial surgeon in a timely manner, who will remove the neoplasm.
How dangerous is a salivary gland tumor?
At first glance, an innocent bump without timely surgery can lead to a fatal outcome: if it is a pleomorphic adenoma, it has a tendency to become malignant and metastasize to the neck lymph nodes, lungs and adjacent tissues. In the best case (the tumor remains benign), the smaller the neoplasm, the easier it is to remove it without damaging the facial nerve.
Ask a Sirius-Dent expert at the consultation